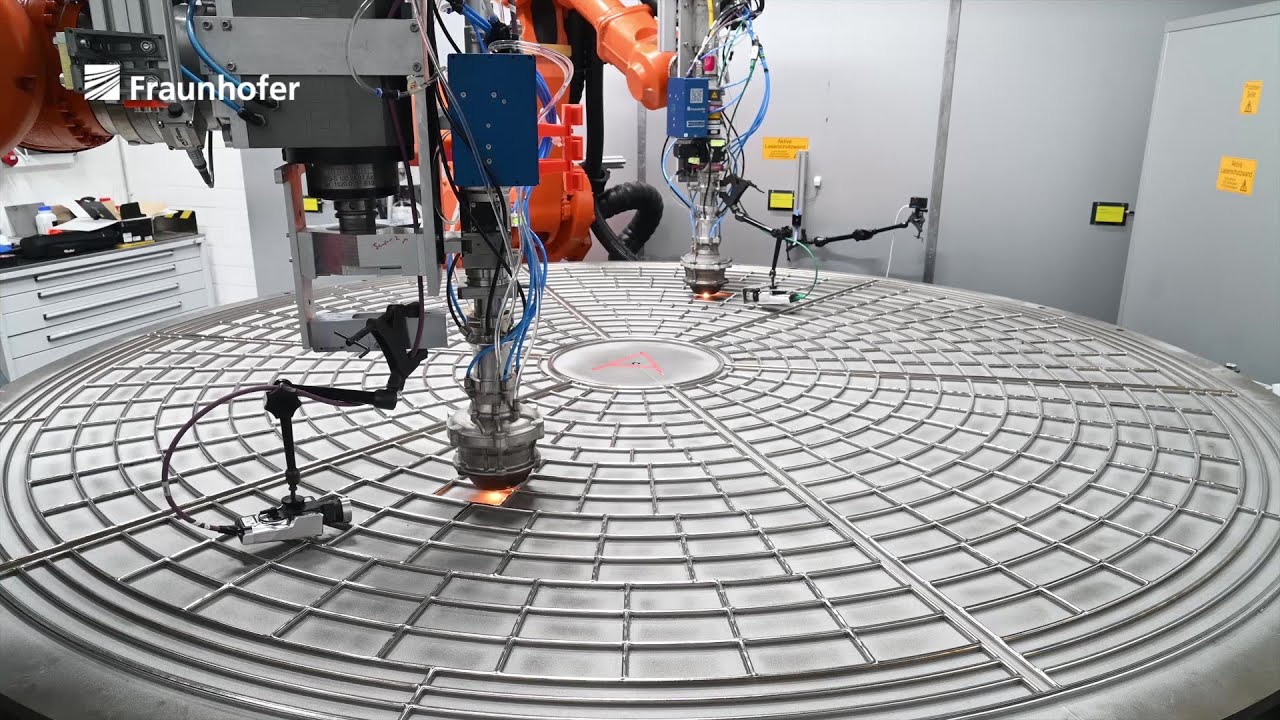
Digital Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing offers enormous potential for the agile and flexible production of customized components from a batch size of one. However, a reproducibly high component quality combined with a low reject rate is a prerequisite for the economic use of the technology and thus its broad establishment. In addition to reliable control of the material and process, this can only be achieved through end-to-end digitalized process management in the sense of Industry 4.0.
Industry 4.0 refers to the intelligent networking of machines and processes in industry by means of information and communication technology. There are many opportunities for companies to use intelligent networking. This includes, for example:
- Flexible production: Many companies are involved in the manufacturing of a product, contributing step by step to its creation. Digital networking allows these steps to be better coordinated and machine capacity utilization to be better planned.
- Adaptable factory: In future, production lines will be built in modules. This allows rapid assembly for a specific task. This improves productivity and efficiency, and enables individualized products to be manufactured in small quantities at affordable prices.
- Customer-centric solutions: Consumers and producers move closer together. Customers themselves can help design products according to their specifications.
- Optimized logistics: Algorithms calculate ideal delivery routes, machines report independently when they need new material - smart networking enables an optimal flow of goods.
- Use of data: Data on the production process and the status of a product is collated and evaluated. Data analysis provides information on how a product can be manufactured more efficiently. More importantly, it forms the basis for completely new business models and services.
- Resource-friendly circular economy: Products are considered over their entire life cycle based on data. The way in which materials can be recycled is already determined at the design stage.
In Additive Manufacturing, this affects not only the automated monitoring of systems (condition monitoring), processes (process monitoring) and component quality (in-line NDT), but also classic and innovative control approaches such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data management for mapping the process and component as a digital representation (Digital Twin).
 Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS
Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS